the quarterly journal of the gemological institute of america
In This Issue
Geology of Corundum and Emerald Gem Deposits
Field Gemology: Building a Research Collection
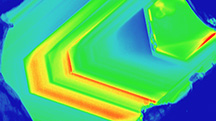
A Review of Analytical Methods Used in Geographic Origin Determination
Geographic Origin of Blue Sapphire
Geographic Origin of Ruby
Geographic Origin of Emerald
Geographic Origin of Paraíba Tourmaline
Geographic Origin of Alexandrite

the quarterly journal of the gemological institute of america
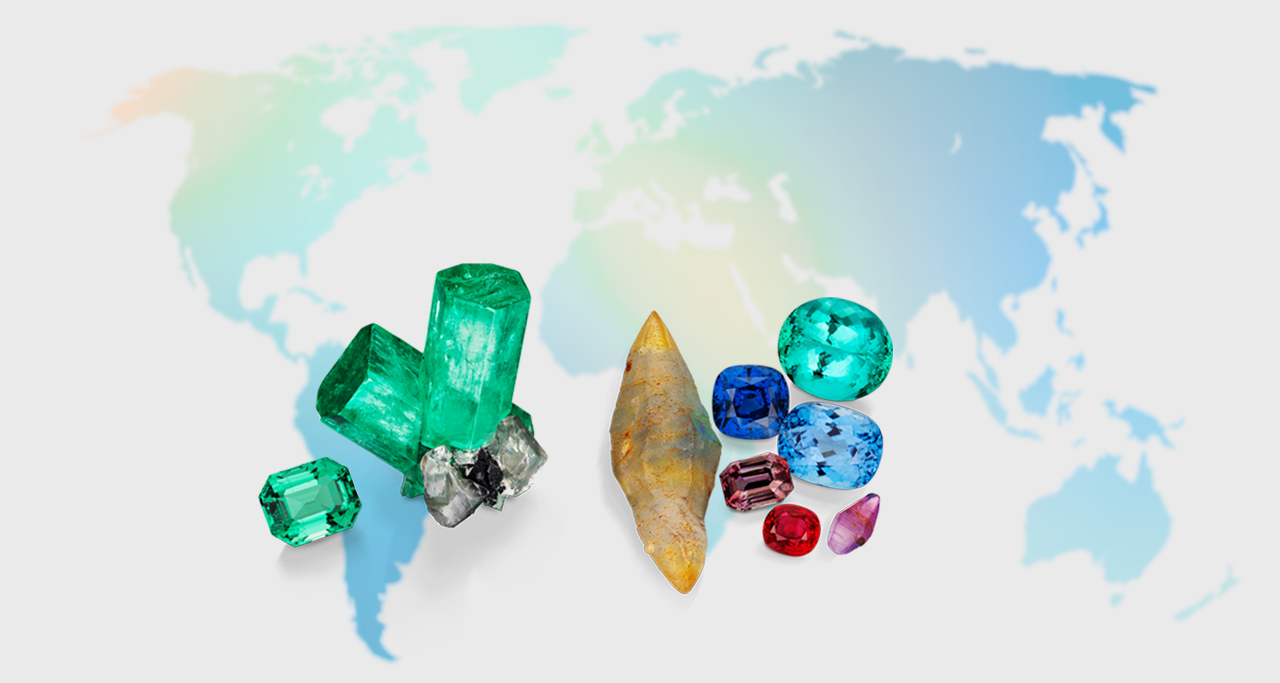

The Geographic Origin Dilemma
Articles (9)

Geology of Corundum and Emerald Gem Deposits: A Review
Over the last two decades, knowledge of the formation of gem deposits has improved significantly. This article reviews the state of our knowledge of the geology and genesis of gem corundum and emerald deposits.
Read More
Field Gemology: Building a Research Collection and Understanding the Development of Gem Deposits
With more than 90 field expeditions on six continents since 2008, GIA has accumulated over 22,000 colored stone reference samples. This extensive collection of colored stones with known origins supports GIA’s research on geographic origin determination.
Read More
A Review of Analytical Methods Used in Geographic Origin Determination of Gemstones
Geographic origin determination relies on a combination of gemological observations and advanced analytical tools. This contribution reviews the analytical methods commonly used to establish origin.
Read More
Geographic Origin Determination of Blue Sapphire
In some cases, the value of a sapphire depends strongly on its geographic origin. This article details the origin data GIA has collected for blue sapphire and describes its methodology for using the data in geographic origin determination.
Read More
Geographic Origin Determination of Ruby
The world ruby market has undergone dramatic change in recent years, especially with the development of ruby mining in Mozambique. This contribution outlines GIA’s methods and criteria for establishing the geographic origin of ruby.
Read More
Geographic Origin Determination of Emerald
The relative chemical diversity of emeralds from different deposits worldwide allows clear origin determination in most cases. This contribution explains the criteria used by GIA to make geographic origin conclusions for emeralds.
Read More
Geographic Origin Determination of Paraíba Tourmaline
Copper-bearing gem tourmaline, known as Paraíba tourmaline after the location of its original discovery, is prized for its vivid blue to green color. This article explains GIA’s use of quantitative chemical analyses to distinguish samples from Brazil, Nigeria, and Mozambique.
Read More
Geographic Origin Determination of Alexandrite
The geographic source of this rare color-change gem has a significant impact on value. Trace element chemistry profiles allow GIA to accurately determine origin for alexandrite from several countries.
Read MoreMOST VALUABLE ARTICLE AWARD

The Color Origin of Gem Diaspore: Correlation to Corundum
Che Shen and Ren Lu

Gemological Characteristics of Sapphires from Yogo Gulch, Montana
Nathan D. Renfro, Aaron C. Palke, and Richard B. Berg

Natural-Color Green Diamonds: A Beautiful Conundrum
Christopher M. Breeding, Sally Eaton-Magaña, and James E. Shigley
the archive
past gems & gemology issues
You Might Also Like

Find a Retailer
learn more
Shop the Campus Store
Learn More
Subscribe to Knowledge Rocks Emails
Learn More